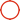
Cold rolling is a manufacturing process used to shape and enhance the properties of stainless steel. It involves passing stainless steel through a series of rollers at room temperature, exerting pressure to reduce its thickness and improve its surface finish. In this section, we will discuss the cold rolling process, different types of stainless steel, and their applications.
Cold Rolling Process:
-
Annealing: The process begins with annealing, where the stainless steel is heated and then slowly cooled to enhance its ductility and remove internal stresses. This step prepares the steel for the subsequent cold rolling process.
-
Cold Rolling: The annealed stainless steel is then passed through a series of rollers that exert pressure to reduce its thickness. This process also improves the mechanical properties of the steel, such as hardness, tensile strength, and yield strength.
-
Skin Pass: After cold rolling, the stainless steel may undergo a skin pass process. This involves a light cold rolling to further improve the surface finish, remove defects, and enhance flatness.
-
Finishing Processes: Finally, the cold-rolled stainless steel undergoes various finishing processes, such as pickling, cleaning, and coating, to remove any impurities, improve corrosion resistance, and achieve the desired surface quality.

Types of Stainless Steel:
-
Austenitic Stainless Steel: Austenitic stainless steel, such as the popular grade 304 and 316, is the most common type used in cold rolling. It is non-magnetic, highly corrosion-resistant, and offers excellent formability and weldability. Austenitic stainless steel finds applications in industries like architecture, kitchenware, medical equipment, and chemical processing.
-
Ferritic Stainless Steel: Ferritic stainless steel, including grades like 430, is characterized by its high chromium content and magnetic properties. It offers good corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, and excellent formability. Ferritic stainless steel is commonly used in automotive components, appliances, and architectural applications.
-
Martensitic Stainless Steel: Martensitic stainless steel, such as grade 410, is known for its high strength, hardness, and wear resistance. It can be hardened through heat treatment, making it suitable for applications that require durability and corrosion resistance, such as cutlery, surgical instruments, and industrial equipment.
-
Duplex Stainless Steel: Duplex stainless steel, such as grade 2205, combines the properties of austenitic and ferritic stainless steels. It offers high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and good weldability. Duplex stainless steel finds applications in chemical processing, oil and gas, and marine environments.
Applications:
-
Architecture and Construction: Cold-rolled stainless steel is widely used in architectural applications, such as building facades, handrails, and decorative elements. Its excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal make it a preferred choice in modern construction.
-
Automotive Industry: Stainless steel is utilized in automotive applications due to its durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic qualities. It is used in exhaust systems, trim components, and structural parts, providing longevity and enhancing the overall performance of vehicles.
-
Food and Beverage Industry: Cold-rolled stainless steel is extensively used in the food and beverage industry due to its hygienic properties, corrosion resistance, and ease of cleaning. It is employed in food processing equipment, storage tanks, and kitchen appliances.
-
Medical and Pharmaceutical Industry: Stainless steel is a vital material in the medical and pharmaceutical sectors. It is used in surgical instruments, medical implants, and pharmaceutical equipment due to its biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and ease of sterilization.
-
Chemical Processing: Cold-rolled stainless steel is employed in chemical processing plants, where corrosion resistance is essential. It is used in reactors, storage tanks, pipelines, and valves, ensuring the integrity and safety of chemical processes.
In summary, the cold rolling process enhances the properties of stainless steel, such as thickness reduction and surface finish improvement. Different types of stainless steel, including austenitic, ferritic, martensitic, and duplex grades, offer various mechanical and corrosion-resistant properties. Cold-rolled stainless steel finds applications in architecture, automotive, food and beverage, medical, and chemical processing industries, where its durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal are highly valued.